



Next: Whitespace Functions
Up: Parsing and Formatting
Previous: Adding And Removing Data
Contents
Subsections
void cut(unsigned long start_idx, unsigned long end_idx);
The cut() function will replace a string with a truncated version. For
performance and to prevent losing stack-based memory, the cut() function
does not reallocate a new smaller string buffer. If you wish to do this, call
compact() after calling cut(). The cut() functions
operates with 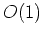 efficiency if cutting only from the right and
efficiency if cutting only from the right and 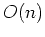 efficiency otherwise.
efficiency otherwise.
Str x = "Hello There";
x.cut(0,5); // x = "Hello"
x = "Hello There";
x.cut(6, x.length()); // x = "There"
x = "Hello There";
x.cut(3, 8); // x = "lo Th"
void copyRange(const Str& str, unsigned long start_idx,
unsigned long end_idx);
The copyRange() function copies a substring from another string
into this one. Do not give the same object as an argument to
copyRange() (i.e. do not call x.copyRange(x,...)). Use
cut() instead.
The copyRange() function will reallocate a new buffer to hold the
substring if (and only if) the current buffer is not large enough to hold
the copy. The copyRange() function operates with 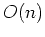 efficiency.
efficiency.
char* buff[8]; // Build y on the stack, just for fun
Str y(buff, 8);
Str x = "Hello There";
y.copyRange(x, 0, 5); // y = "Hello", buff = "Hello"
y.copyRange(x, 7, x.length()); // y = "here", buff="here"
y.copyRange(x, 1, x.length()); // to big for buff, y = "ello There", buff="here"
2007-05-05